crm account essentials for modern business growth are foundational for any organization aiming to build meaningful connections and streamline customer interactions. A crm account is much more than just a dataset—it’s a powerful tool that helps businesses keep track of every interaction, manage valuable information, and pave the way for smarter decision-making.
From understanding various types of crm accounts to exploring how each structure, data field, and integration impacts daily operations, mastering crm account management unlocks the potential for better collaboration, secure data handling, and actionable insights. Whether you’re setting up your first crm account or refining your existing process, knowing the best practices and staying ahead of trends can give your business a competitive edge.
Definition and Purpose of CRM Account
A CRM account refers to a dedicated record within a customer relationship management (CRM) platform that represents an organization, business, or individual with whom a company has, or aims to establish, ongoing business interactions. CRM accounts are the core units for organizing all information, activities, and communications related to a particular customer or partner. Their purpose is to centralize and streamline management of customer data, making it easier for teams to deliver personalized services, track sales opportunities, and build lasting relationships.
Within CRM systems, accounts serve several essential functions, acting as the central hub where all relevant contact details, historical interactions, sales activities, and service requests are stored. This enables teams across sales, marketing, and support to access up-to-date information and collaborate efficiently.
Core Functions of a CRM Account
CRM accounts are fundamental to the structure of customer relationship management. They ensure that customer data is not siloed and that all departments can work from the same source of truth.
- Centralize customer or partner data for unified access.
- Link related contacts, deals, activities, and support cases.
- Enable tracking of account status and communication history.
- Support segmentation and targeted outreach based on account attributes.
- Facilitate reporting on account activity, performance, and value.
Key Elements of a CRM Account
The following elements commonly make up a CRM account record, providing a complete picture of each customer or partner relationship.
- Account Name
- Account Type (e.g., Customer, Partner, Prospect)
- Primary Contact Information
- Industry and Business Details
- Account Status and Lifecycle Stage
- Assigned Owner or Team
- Associated Opportunities, Activities, and Support Cases
Types of CRM Accounts
CRM systems accommodate various types of accounts to reflect different business relationships. Recognizing these distinctions allows organizations to better organize their data and tailor engagement strategies.
Comparison of CRM Account Types
Each account type serves different business needs, and choosing the right structure enhances both user experience and reporting accuracy.
| Account Type | Features | Ideal Use Case | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Individual Account | Personal contact data, one-on-one relationships | B2C companies, personal clients | Independent consultant, retail customer |
| Corporate Account | Multiple contacts, business hierarchy, organization-wide data | B2B sales, enterprise clients | Large manufacturing company |
| Partner Account | Collaboration data, joint opportunities, shared marketing | Channel partners, resellers | IT solution provider partnership |
Common Scenarios for CRM Account Types
Businesses benefit when they map account types to real-world scenarios, ensuring that the CRM mirrors actual customer and partner relationships.
- Individual accounts are ideal for retail or service businesses where customers are private individuals, such as in fitness coaching or online retail.
- Corporate accounts fit for B2B companies dealing with teams or departments within larger organizations, such as SaaS vendors or industrial suppliers.
- Partner accounts streamline collaboration with other businesses for co-marketing, joint sales, or distribution agreements, such as in franchising or technology alliances.
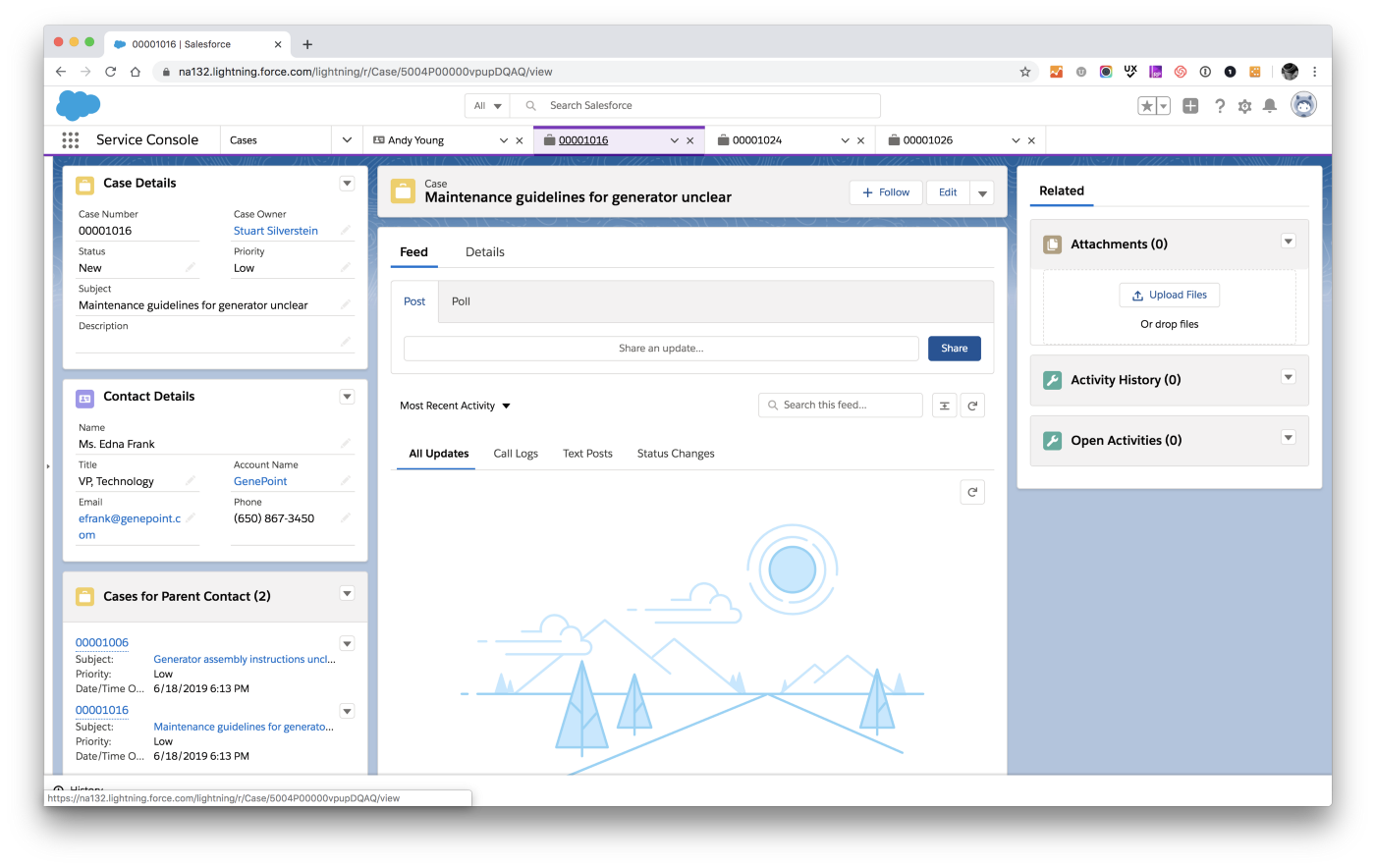
CRM Account Structure and Data Fields
Every CRM account is defined by a standard set of data fields, which capture critical information necessary for effective relationship management. These fields can be customized to suit specific business requirements and industries, allowing companies to track relevant data points.
Common Data Fields in CRM Accounts
The structure of a CRM account typically covers core identifier and status fields, as well as relationship mapping to contacts and business activities.
| Field Name | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| Account Name | Main identifier for the organization or individual | Acme Corporation |
| Account Type | Classifies the account (e.g., Customer, Prospect, Partner) | Customer |
| Industry | Industry sector of the account | Healthcare |
| Status | Current stage or condition (e.g., Active, Inactive) | Active |
| Primary Contact | Main point of contact’s name and details | Jane Foster, [email protected] |
| Account Owner | Assigned employee or team handling the account | Michael Tan, Sales Team A |
| Location | Geographical address of the account | 123 Business Ave, Singapore |
Importance of Customizing Account Fields
Customizing CRM account data fields ensures that organizations capture information relevant to their unique sales cycle, industry, or compliance needs. For instance, an insurance company might add policy expiration dates, while a tech startup may require integration status fields. Custom fields help tailor reports, automate processes, and empower teams to focus on metrics that matter.
Setting Up and Managing CRM Accounts
Effectively setting up and managing CRM accounts is crucial for data integrity and operational efficiency. A well-organized process reduces errors, prevents duplication, and supports business growth.
Steps in Creating a New CRM Account
Creating a new account involves several essential steps. Following a structured approach minimizes mistakes and lays the foundation for reliable data.
- Login to your CRM platform with appropriate permissions.
- Navigate to the “Accounts” or “Organizations” module.
- Select the “Create New Account” or “New Record” option.
- Enter key details: account name, type, industry, contact info, and owner.
- Add any custom fields as needed for your business requirements.
- Link related contacts, opportunities, and activities.
- Save the record and set up automations or alerts if applicable.
Best Practices for Account Data Entry and Maintenance
Adhering to best practices in data entry and ongoing management ensures the CRM remains a valuable, trustworthy resource.
- Validate information before data entry to avoid duplicates.
- Use standardized naming conventions for consistency.
- Regularly audit account data for completeness and accuracy.
- Keep account statuses updated to reflect real-time changes.
- Provide training so all team members understand data entry protocols.
Merging Duplicate Accounts and Managing Hierarchies
Duplicate accounts can cause confusion and reporting issues. Most CRM systems offer built-in tools for identifying and merging duplicates, while account hierarchy features help represent parent-child or multi-location relationships.
- Use duplicate detection tools to identify overlapping account records.
- Merge duplicates by consolidating data, preserving historical activities, and updating links to contacts and deals.
- Utilize account hierarchy features to set up parent and child accounts, reflecting real-world corporate structures.
- Regularly review hierarchies to ensure organizational changes are reflected in the CRM.
CRM Account Roles and Permissions
To maintain data security and proper collaboration, CRM platforms use role-based permissions to control who can view, edit, or manage accounts. Assigning the appropriate roles ensures sensitive information is protected while allowing teams to work effectively.
User Role Interactions with CRM Account Data
Different user roles within a CRM system have varying levels of access and responsibilities. The following table illustrates how permissions are typically structured.
| User Role | Access Level | Allowed Actions | Collaboration Scope |
|---|---|---|---|
| System Admin | Full access | Create, edit, delete, assign accounts | All accounts and settings |
| Sales Manager | Team-level access | View, edit, assign within team | Team accounts |
| Sales Rep | Owned accounts | View, edit, update assigned accounts | Personal accounts |
| Support Agent | Case-linked accounts | View account info, log support activities | Accounts linked to open cases |
Balancing Security and Collaboration
A balanced permission structure helps organizations protect confidential data while enabling cross-department collaboration. Strategies include:
- Implementing role-based access with granular permissions.
- Limiting sensitive fields to senior staff or management only.
- Using audit trails to monitor account access and changes.
- Granting temporary elevated access for cross-team projects.
Integrating CRM Accounts with Other Business Functions
CRM accounts are most valuable when integrated with key business processes, connecting sales, marketing, and customer support workflows for a seamless customer experience.
Account Data Integration in Business Workflows
Integrating CRM accounts enables automation and deeper insights across teams. Example workflows that rely on connected account data include:
- Sales pipeline updates triggering marketing email sequences based on account status.
- Customer support cases automatically visible to assigned account managers for faster issue resolution.
- Marketing campaign responses recorded at account level for ROI tracking and lead scoring.
Methods for Syncing Account Information with Third-Party Applications
To enhance business agility, CRM platforms often provide tools and APIs for syncing account information with external systems, such as ERP, marketing automation, or helpdesk software. Popular methods include:
- Pre-built integrations for popular tools like Mailchimp, Zendesk, or QuickBooks.
- Custom API connections for real-time data exchange between CRM and other platforms.
- Automated data import/export processes for batch updates.
- Webhooks that trigger actions in third-party apps when account records are updated.
Key Metrics and Reporting for CRM Accounts
Tracking the right key performance indicators (KPIs) is vital for evaluating account health and understanding customer value over time. CRM systems provide robust reporting and dashboard tools for this purpose.
Essential CRM Account KPIs
The following table Artikels core KPIs tracked through CRM accounts, along with their definitions and recommended reporting frequency.
| KPI | Definition | Reporting Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Account Activity Rate | Number of interactions or touchpoints per account | Weekly/Monthly |
| Account Lifetime Value (LTV) | Total revenue generated from an account over its relationship period | Quarterly/Annually |
| Opportunity Win Rate | Percentage of deals closed from opportunities linked to an account | Monthly/Quarterly |
| Case Resolution Time | Average time taken to resolve support cases per account | Weekly/Monthly |
Visualizing CRM Account Performance
Dashboards and interactive charts are commonly used to visualize account metrics, helping managers identify trends, spot at-risk accounts, and allocate resources more effectively. Common visualizations include bar graphs for activity rates, pie charts for opportunity outcomes, and line graphs showing lifetime value growth.
Challenges and Considerations in CRM Account Management
Despite their advantages, managing CRM accounts presents several challenges, particularly related to data integrity and user engagement. Addressing these is key to maximizing CRM investment.
Common Challenges in CRM Account Management
Organizations typically encounter the following issues when managing CRM accounts:
- Incomplete or inaccurate account data due to inconsistent entry.
- Duplicate records from multiple team inputs or system migrations.
- Low user adoption because of complex or unintuitive interfaces.
- Security risks from improper permission settings.
- Difficulty maintaining account hierarchies as businesses grow and restructure.
Practical Solutions for CRM Account Challenges
By proactively addressing these issues, businesses can improve CRM effectiveness and user satisfaction.
- Establish clear data entry guidelines and provide regular training.
- Automate duplicate detection and data validation processes.
- Customize the CRM interface and workflows to align with user needs.
- Regularly audit user permissions and account access logs.
- Assign dedicated admins to manage account hierarchies and mergers.
Impact of Account Mismanagement
Mismanaged accounts can lead to lost sales opportunities, poor customer experiences, and compliance risks, ultimately impacting business reputation and profitability. Ensuring robust account management practices is therefore critical for sustainable growth.
Future Trends in CRM Account Management
The landscape of CRM account management is rapidly evolving as new technologies and customer expectations reshape how businesses engage with their clients. AI-driven insights, automation, and enhanced integrations are setting new standards for what CRM accounts can achieve.
Emerging Technologies in CRM Accounts
Modern CRM platforms are adopting features such as predictive analytics, AI-powered lead scoring, and automated workflow triggers. For example, Salesforce Einstein and Microsoft Dynamics 365 are leveraging machine learning to recommend next best actions for accounts, while automation tools handle routine updates and reminders.
Innovative Features Enhancing Account Management
Key advancements being rolled out in leading CRM systems include:
- Real-time collaboration tools allowing multiple users to update accounts simultaneously.
- Automated data enrichment using public and private data sources.
- Voice and chat integrations for instant account updates from anywhere.
- Enhanced mobile interfaces for field teams to manage accounts on the go.
The future of CRM accounts lies in intelligent, adaptive systems that automatically surface critical insights, proactively suggest opportunities, and seamlessly connect account data across every customer touchpoint. Organizations that harness these technologies will be well-positioned to deliver hyper-personalized experiences and drive sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Final Summary
In summary, managing a crm account effectively is key to driving strong customer relationships, supporting business functions, and adapting to future trends. By focusing on organization, security, and integration, businesses can turn account data into a strategic asset and fuel long-term growth in an ever-evolving marketplace.
FAQ Corner
What is a crm account?
A crm account is a digital record within a customer relationship management system that stores essential information about a client, company, or partner, making it easier to manage interactions and track business activities.
Why do businesses need crm accounts?
Crm accounts help businesses organize customer data, personalize communication, monitor sales and support activities, and improve overall efficiency in managing relationships.
Can crm accounts be customized for different industries?
Yes, most crm platforms allow you to add or modify data fields and workflows so the account structure fits your unique industry requirements.
How do crm accounts improve sales and marketing?
By centralizing customer details and purchase history, crm accounts enable targeted marketing, track sales pipelines, and help sales teams follow up on opportunities more effectively.
Is it possible to restrict access to crm accounts?
Absolutely. Roles and permissions can be assigned so only authorized users can view or edit certain account information, ensuring data privacy and security.
